SEEKING TRUTHS
(The following is adapted from my most recent book, The Ever Curious Gardener: Using a Little Natural Science for a Much Better Garden, available from the usual outlets or, signed, from here.)
OBSERVE AND ASK
Charles Darwin did some of his best work lying on his belly in a grassy meadow. Not daydreaming, but closely observing the lives and work of earthworms, eventually leading to the publication of his final book, The Formation of Vegetable Mould through the Action of Worms. He calculated that these (to some humans) lowly creatures brought 18 tons of nutrient-rich castings to the surface per acre per year, in so doing tilling and aerating the soil while rendering the nutrients more accessible for plant use.

We gardeners can also take a more scientific perspective in our gardens without the need for digital readouts, flashing LEDs, spiraling coils of copper tubing, or other bells and whistles of modern science. What’s most needed is careful observation, an eye out for serendipity, and objectivity.
Observation invites questions. How many tons of castings would Darwin’s earthworms have brought to the surface of the ground in a different soil? Or from soil beneath a forest of trees rather than a grassy meadow?
And questions invite hypotheses, based on what was observed and what is known. Darwin’s prone observations, along with knowledge of soils, earthworms, plants, and climate, might invite a hypothesis such as “Earthworms would bring a greater amount of castings to the surface in a warmer climate.” Is this true? How can we find out?
MAKE A HYPOTHESIS
Gardens are variable and complex ecosystems, which makes growing plants both interesting and, if you want to know why a plant did what it did, frustrating. Many gardeners do something — spraying compost tea on tomatoes to reduce disease, for example — and attribute whatever happens in the ensuing season to the compost tea, ignoring the something else, or combination of things, that might also have made contributions to whatever happened.
Enter the scientific method, a way to test a hypothesis. You put together a hypothesis by drawing on what is known and what can be surmised. In spraying compost tea, your hypothesis, could be based perhaps on the idea that beneficial microbes in compost tea could could fight off pathogens, just as they do in the soil. (Many gardeners do, in fact, recommend compost tea for plant health. Do I? See https://leereich.com/2015/03/compost-tea-snake-oil-or-plant-elixir.html.)
Less disease on your sprayed plants would strengthen the case for further study. Why further study? Because the response of plants in a given season at a given location is not sufficient to make a general recommendation or make a theory.
The way to truly assess the benefit of the spray is to subject it to scientific scrutiny: Come up with a hypothesis, such as “Compost tea reduces tomato leaf diseases,” and then design an experiment to accurately test the validity of the hypothesis.
DESIGN AN EXPERIMENT
A well-designed experiment would need more than just one treated (compost tea sprayed) plant and one control (water sprayed) plant. Grow ten tomato plants of the same variety under the same conditions and some will grow a little more than the others, some a little less. With too few test plants, natural variation in growth from plant to plant might overwhelm any variation due to a treatment (spraying with the tea in this example). Given enough plants to even out the natural variations in, say, disease incidence, the effects of a treatment can be parsed out. Greater natural variations would require more plants for the test.

A garden experiment might have additional sources of variation. Perhaps one side of your garden is more windy, or the soil is slightly different, or basks plants in a bit more sunlight than the other side. Rather than have all the treated plants cozied together growing better or worse because of this added effect, even out these effects by randomizing the locations of treated and control plants.
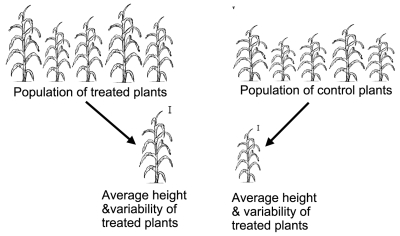
Now we’ve got an experiment! All that’s needed is to spray designated plants with either the compost tea or the water, and then take measurements. Plug those measurements into a software program for statistical analysis and a computer will spew out a percent probability, based on variability within and between each group of plants, that the tea was responsible for less disease. A test with 90% or 95% probability is usually considered sufficient to link cause and effect. You can then answer “yea” or “nay” to the hypothesized question; you now have a theory, or not.
IS IT SIGNIFICANT?
A good test could involve a lot of plants and a lot of measurements, more than most of us gardeners are willing to endure. A danger exists, as Charles Dudley Warner so aptly put it in his 1870 book, My Summer in a Garden: “I have seen gardens which were all experiment, given over to every new thing, and which produced little or nothing to the owners, except the pleasure of expectation.” Then again, setting up something less than a full-blown experiment could be fun and, while not proving something to a 95% confidence level, still suggest a possible benefit.
Knowing what’s involved in testing a hypothesis also increases appreciation for all that can affect plants. Perhaps your tomato plants’ vibrant health wasn’t from your compost spray. Knowing something of the scientific method can help you assess, whether observed in your own garden or a friend’s garden, or reported in a scientific journal, the benefit of the spray.
So go out to your garden and look more deeply into Nature, perhaps, like Darwin, lying on your belly. Understanding some of the science at play in the garden takes it to the next level. And you’ll find that the real world, neatly woven together, is imbued with its own poetry, with science being one window into that poetry.

Me mulching, even as a beginning gardener


Looks like a broad-headed planarian in the illustration (they are also invasive here and prey on earthworms) don’t think they do all that much for soil aeration and mould production though
Geez, you’re right. Well, I didn’t take credit for the drawing.