My Garden’s A Mess!
After some really frigid weather a month ago followed by more or less seasonal cold, temperatures did a loop de loop and we’ve had a couple of days in the high ‘60s. Very unseasonal, to say the least, and perhaps another indication of global warming, but welcome nonetheless. Those temperatures, coupled with brightening sunshine, made me want to get my hands in some dirt.
A large, second-story bedroom window overlooks my main vegetable garden. The weather made me see it in a different perspective — it looked messy.
I pride myself on putting everything in order each fall so that (quoting from Charles Dudley Warner’s 1886 My summer in the Garden) “The closing scenes are not necessarily funereal . . . A garden should be got ready for winter . . . neat and trim. . . in complete order so that its last days shall not present a scene of melancholy ruin and decay.”

Not a pretty picture

Endive, dead in January
Although I had mostly cleaned up spent vegetables and dressed the beds with an inch-deep layer of compost, early wintry weather put an end to that. Now, what I saw outside was too much “melancholy ruin and decay” from a few beds of late cabbages and their kin and tunneled beds of endive. The wilted, dried, browned leaves of unharvested endive lay flat, covering those beds.
Spring-like temperatures offered me the opportunity to get my hands in the dirt. I grabbed my hori-hori knife and gathered up frozen or dessicated leaves and plants for carting over to the compost pile. What a shock to even find some signs of life still out there in the beds: some arugula, some kale plants, and a couple of plants of baby pak choy and michili Chinese cabbage.


Coldest temperatures (minus 20 degrees F. here) typically arrive in late January. Those temperatures will do in these plants. Except for mâche, of course, which was also still alive in the garden, spry and green as if temperatures had never already dropped near zero, and which always survives winter.

Mache, in garden in January

Garden after cleanup
First Seeds
That spring-like weather also gave me the urge to sow some seeds. These would be the first of the year, a seed flat of lettuce and baby pak choy to mature in early spring in the greenhouse. For some irrational reason, I’m never that confident that those tiny specks are actually going to sprout, even though I’ve done this successfully for decades.
Perhaps my lack of faith comes from my first experiences sowing seeds. That was many years ago when, as a graduate student, I lived in a motel room that had been converted into an apartment and began my first garden as an adult. I sowed all sorts of vegetable and herb seeds in peat pots that I set in trays on a shelf on a wall near a window.
All those seedlings died — and that was my abrupt introduction to “damping off,” a disease that attacks seeds and newly emerged seedlings. Imagine the disappointment of a beginning gardener (me) watching seedling stems pinch in at he soil line and topple over — the telltale symptom of damping off disease.

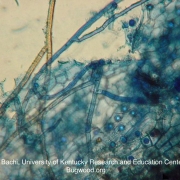
First Disease
I soon learned that damping off was not uncommon, even among experienced gardeners. The disease is caused by any one of a few soil dwelling fungi that raise their ugly head (figuratively) given the right conditions (for them). One obvious way to try to avoid the problem is to sterilize the potting media.
Most commercial potting mixes are sterile, as were the peat pots I was using. The problem is that the culpable microbes are everywhere, waiting to attack when conditions are just right, conditions that I unknowingly provided in my motel room. The peat pots were excessively moist; the air stood still; and little light entered the room — perfect for damping off development.
Nowadays, my seedlings rarely experience damping off. The plants get off to a good start at temperatures they enjoy, bathe in light in my greenhouse or sunny windows (or, in the past, cozied up very close to fluorescent bulbs), and a fan keeps the air moving. I also add sufficient perlite to my potting mixes so that excess water drains feely down and out of the mix. A thin layer of well-draining material, such as sand or calcined montmorillonite clay (kitty litter) can also help.
Years ago, soothing brews of chamomile tea would also come to the rescue — for the seedlings, not for me. That tea hasn’t been needed for a long time. I also don’t pasteurize or sterilize my potting mixes. Beneficial microbes, from the compost in my mix, and good growing conditions have thankfully made damping off nothing more than a distant memory for me.











 My plan is to sacrifice the coral bells and pull out every rhizome I can find. In soft soil this time of year, long pieces can be lifted with minimum breakage or soil disturbance. A mulch with a few layers of newspaper, topped with a wood chip mulch (part of weed management, as described in my book Weedless Gardening) will suffocate any overlooked rhizome pieces trying to sprout. In the absence of other plants among which the rhizomes could sprout, mulching alone can do in quackgrass, as it did in my second garden.
My plan is to sacrifice the coral bells and pull out every rhizome I can find. In soft soil this time of year, long pieces can be lifted with minimum breakage or soil disturbance. A mulch with a few layers of newspaper, topped with a wood chip mulch (part of weed management, as described in my book Weedless Gardening) will suffocate any overlooked rhizome pieces trying to sprout. In the absence of other plants among which the rhizomes could sprout, mulching alone can do in quackgrass, as it did in my second garden.

