SOWING PEARS AND LETTUCES
For the Long Haul
Among the must-have tools for any good gardener are hope, optimism, and patience. I thought of all three last week as I was planting some seeds.

The first of these seeds especially emphasizes patience. They were a few pear seeds I saved from pears I had eaten. After being soaked for a couple of days in water, the cores were soft enough for the seeds to be squeezed out, after which they were rinsed, and then planted in potting soil.
I put the planted seeds near a bright window in my basement where the cool (about 40°) temperatures would, in a couple of months, fool the seeds into feeling that winter was over. They would sprout.

Given time, those seeds would grow to become pear trees and, given more time (ten years, possibly more) go on to bear fruit. Those seeds came from Bosc and Passe Crassane pears. The genetics of the resulting trees will represent the sexual union of egg cells within the flowers with whatever male pollen happened to fertilize those eggs. As a result, said trees would bear fruits different, and probably worse, than the fruits from which they were taken. (There’s less than 1 in 10,000 chance of a seedling apple tree bearing fruit as good or better than the fruit from the mother tree; the ratio for pears should be similar.)
Shortening the Long Haul, and Other Benefits

Grafted tree, this one NOT interstem
So why will I be wasting all that time nurturing these plants? Because they’re not for fruit. They’re for rootstocks, for grafting. Pears and most other tree fruits are very hard to root from cuttings, so are propagated by grafting a stem of a good-tasting pear low on a rootstock.

So-called “seedling” rootstocks make for very sturdy trees, well anchored and genetically diverse so some scourge can’t wipe out a whole bunch of equally susceptible, genetically identical trees. On the other hand, seedling rootstocks make for very large trees that are very slow to induce bearing in their grafted portions.
Enter from stage right: clonal rootstocks, that is, plants reproduced asexually (cuttings are one example of asexual plant propagation) so that all members of the clone are genetically identical. Some clonal pear rootstocks — with such unalluring names as Pyrodwarf and OH x F 87 — have been developed that make smaller grafted trees that also are quicker to come into bearing. (I delve more deeply into the nitty gritty of grafting in my book The Ever Curious Gardener: Using a Little Natural Science for a Much Better Garden.)
My plan is to make interstem trees, each one by grafting a 9 inch stem of one of the clonal rootstocks near the base of a seedling rootstock, and then some variety for eating, such as Passe Crassane, atop the clonal interstem. That 9 inch clonal interstem has the same good effects as if it was used as a rootstock, except that the interstem trees also have sturdy root systems and genetic diversity at their roots. Because plants grow from the tips of stems, the heights of the grafts above ground remain the same even as the tree grows.
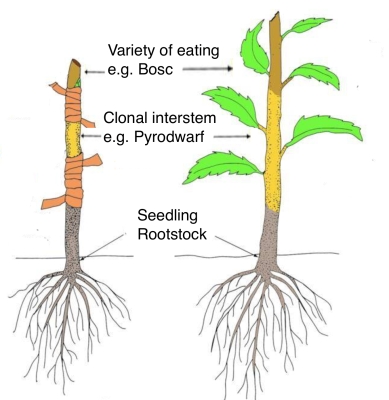
Parts of interstem tree
I’ll do both grafts at the same time, next spring. I’m hopeful, optimistic, and have patience that I’ll be biting my first pears from these trees within 5 years.
Lettuce be Hopeful, Patient, and Optimistic
The other seeds for this week’s sowing were four varieties of lettuce. No, not for eventual outdoor planting, but for planting in the greenhouse in spaces that will open up where some of last autumn’s lettuce will have been harvested.
It’s chilly in the greenhouse, where temperatures drop into the 30’s at night and on cloudy days, too chilly for good sprouting of lettuce seeds.  So I sowed them in a 4×6 inch seed flat filled with potting soil, then moved the flat in front of a sun-drenched, living room window. Once the lettuce seeds sprouted, which was in a few days, I moved them to the greenhouse. Warmer temperatures are needed to sprout a seed than to grow a plant.
So I sowed them in a 4×6 inch seed flat filled with potting soil, then moved the flat in front of a sun-drenched, living room window. Once the lettuce seeds sprouted, which was in a few days, I moved them to the greenhouse. Warmer temperatures are needed to sprout a seed than to grow a plant.

The seedlings should not, of course, remained crowded in their mini-furrows in the flat. So once the seedlings grow a little larger, I’ll gently lift each one by its leaves, coaxing it up and out of the flat, and then lower the roots into a dibbled hole in one potting-soil-filled-cell of GrowEase. And so on, until each of the 24 cells has a small plant in it.
 I use this same method to keep up a steady supply of lettuce and other seedlings all through summer, the plants typically needing about a month in the GrowEase before they’re ready to transplant into the ground. Not so in winter, with the sun still hanging low in the sky and greenhouse temperature still cool. I estimate that it won’t be until early March before the lettuces will be ready to plant in the ground in the greenhouse.
I use this same method to keep up a steady supply of lettuce and other seedlings all through summer, the plants typically needing about a month in the GrowEase before they’re ready to transplant into the ground. Not so in winter, with the sun still hanging low in the sky and greenhouse temperature still cool. I estimate that it won’t be until early March before the lettuces will be ready to plant in the ground in the greenhouse.
No matter; I’m hopeful, optimistic, and patient. And I’ll still be harvesting some of last autumn’s lettuce beyond that date.






Have you ever published articles or books that talk about greenhouses for newbies? I am considering building one this year and need all the help I can get to understand how best to lay it out and deal with the seasons.
Hi Steve, No, I haven’t written that much about greenhouses only because most of my readers don’t have one and aren’t planning on one. Feel free to contact me if you have any specific questions. My main advice is: Don’t make it too small. Besides offering less room for growing plants, in a small greenhouse, too much of the interior is unduly cold because of its proximity to outside edges.
Steve,
There is a national organization called the hobby greenhouse association, probably with an associated social media account. You should be able to get lots of help there.If you have a decent budget, consider using a good company like alit or Hartley botanic. Pricey but well worth it. We have one of each, which are glass. You could go with polycarbonate and do very well.
I too have searched for such a book. In addition I wonder what really is the difference between a cold frame and an unheated greenhouse. The only book I could find in the library suggested an unheated greenhouse was only 3 season use.
With more volume of air to cool dosn, temperatures stay warmer.
Thank you Lee. So interesting.
Hi Lee, Ive been grafting small scion sections of just a few buds because… thats how Ive done it?
Is there a benefit to the longer 9 inch scion? More stored energy or something? I would think it would be more likely to break off w wind or getting knocked (longer lever and all that).
You can make a graft with even one bud, using a bud graft. The reason I specified 9″ is because that’s the length of dwarfing interstem needed for its effect on the variety grafted above it. If I use shorter interstem scion, I would have to let it grow a season before grafting it to the eating variety. By using a 9″ interstem, I can do both grafts at the same time, and save a year.
Aha! That makes sense. So you are on quince/comice with another on top. Got it!
No, not “on quince/comice with another on top,” but similar concept. I have seedling/P233 or seedling/OHxF97 with another top.
Did January 27th sub zero (-3 in Germantown) hurt your new pear seedlings? How did you protect them, but allow sunlight?
-8 here in the Wallkill Valley. The seedlings should be fine to well below that temperature. The seeds I planted would also be fine. The only things that would get damaged would have been young seedlings that had just sprouted, which would not normally happen outdoors.
Hi Lee: I was revisiting archived articles on onions and your potting soil mix recipe. When you start seeds of something that will stay in the one pot for several months, is the compost enough, or do you add something to the mix or fert with liquid as you go? I so appreciate that you are willing to answer questions.
Thank you,
Kari H.
I often add some soybean meal to my potting mix, about a cup per 10 gallons. The soy meal is a long-term, slow release, organic supplier of nitrogen, which is the only extra nutrient that would be needed in my mix.
Around here there are legions of wild callery pears growing in every ditch and unattended field.
Can I ask why you’re planting a seedling instead of digging up and grafting to a callery pear? I’ve found them to be excellent pear rootstocks.
Good question. It’s billed as not very cold hardy. But there are oodles of seedlings around here. I guess I’d have to go and dig up some pencil thick seedlings. I could do that; I know of a despised patch of them nearby. (They’re somewhat/quite invasive because of all the ornamental callery pears tht have been planted.
Sorry I somehow had missed the last 2 paragraphs which answered my question. Just saw it now
Lee, I am wondering about growing greens indoor under lights for winter eating. Is this a waste of time, or do you think I could do leaf lettuce to an edible size? We eat a lot of greens, and the supermarket stuff is expensive and downright ugly. And at -8 this morning, no way to grow outside even if I did have a greenhouse!
It is possible, under lights, provided you provide plenty of light and other good growing conditions. I would look into LED lights for indoor growing.