ROSES AND STRAWBERRIES AND — OH NO! — HONEYBERRIES
Roses, Oh Yes
I bake really good bread, but “man can’t live by bread alone.” Sometimes, you’ve got to “stop to smell the roses.” Enough with the quotations! But back to the roses.

A love of roses has crept up on me over the years, due mostly to changes in kinds of roses available. Up until about 30 years ago, hybrid teas were pretty much the only roses on the block. These plants’ gangly stems are each capped by a vividly colored, fairly stiff, formal blossom whose petals wrap together into a pointy peak. You see where I’m going: hybrid teas are ugly, to me at least.
Also available were grandiflora and floribunda roses. Grandifloras are like hybrid teas, except their stems end with clusters of a few, but smaller, blossoms. Floribunda roses have even larger flower clusters of even smaller flowers. Despite being bushes more full with flowers than hybrid teas, grandiflora and floribunda flowers are still rather prim and proper except for their traffic-stopping colors.
Then so-called species and old-fashioned roses entered the scene, roses that are as nature made them or only slightly hybridized. These roses constitute broad groups, but generally, what they have going for them are more subdued — think pastel — colors and more blowsy blossoms on more heavily branching, fuller-bodied, shrubs.
The downside to species and old-fashioned roses, even if you like their blossoms and their growth habits, is that many bloom only in the spring. Hybrid teas pump out blossom after blossom all summer long.

Rose d’Ipsahan
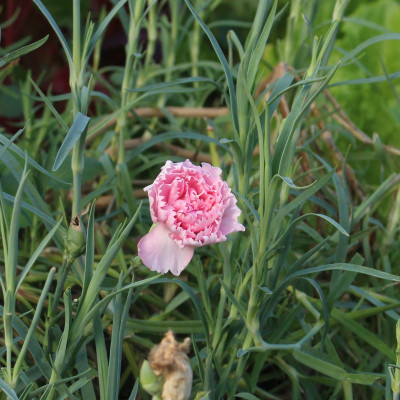
Enter Rose de Rescht, my first old-fashioned rose, given to me by a local, fellow gardener. Ann told me that this rose variety had soft pink flowers and heavenly scent. She was right about the appearance and fragrance, wrong about the name. After years of sleuthing, I’ve identified the rose as Rose d’Ispahan, probably originating in Persia but first discovered in a garden in Isfahan, Iran, renowned for its gardens and roses.
If I had to grow only one variety of rose, Rose d’Ispahan would be the one, for the beauty of its flowers, for its intense fragrance, for its cold-hardiness, for its lack of large thorns, and for its pest resistance. And that’s even though it blossoms only in spring. (It does so over a long period, though.)

Rose d’Ipsahan
But I don’t have to grow only one variety of rose. My other favorites are some of rose breeder David Austin’s varieties which combine the pest resistance and repeat blooming of modern roses with the blowsy, fragrant, pastel colored blossoms and full-bodied shrubs of old fashioned roses. My currant, and perhaps all-time, favorites are Lady of Shallot and, in my opinion needing a more euphonious name, Golden Celebration.

Golden Celebration rose
Both sport yellow — no, Golden! — blossoms, some apricot in those of Lady of Shallot, and a rich yellow, all contained in a petal-filled cup-shape in those of Golden Celebration. Another of my favorites, Lady Judi Dench, never woke up in spring a year ago; perhaps it was the cold, perhaps something else.

Lady of Shallot rose
I also grow another David Austin Rose, LD Braithewaite, with deep red blossoms and dark green, slightly reddish leaves. Not my favorite as far as appearance but this rose is very cold hardy and pumps out tons of blossoms almost all season long.

LD Braithewaite rose
And Strawberries, Oh Yes
 On to strawberries. I’m growing three kinds: the Pineapple Crush variety of white alpine strawberries; the Earliglow variety of garden strawberry; and a few varieties of vescana strawberries, which are hybrids of garden and alpine strawberries. This also is the order, starting with the best, of flavor for the three types.
On to strawberries. I’m growing three kinds: the Pineapple Crush variety of white alpine strawberries; the Earliglow variety of garden strawberry; and a few varieties of vescana strawberries, which are hybrids of garden and alpine strawberries. This also is the order, starting with the best, of flavor for the three types.
Why do I grow anything but the best? Because alpines are so small that it’s hard to fill a bowl with them. I grow vescanas, for the first time this year, because I never grew them before.
The Earliglow berries taste good and do quickly fill a bowl, ideally yielding one quart of berries per plant over the course of the season. Except this year, a problem has surfaced. Leather rot is a fungal disease (Phytophthora cactorum) that rears its ugly head — infected berries that taste bitter and have white patches that turn brown — usually following excessively wet periods from late spring to early summer, which is odd because weather has been on the dry side. Also odd because I’ve never seen the problem here before.


Which brings me back to vescana and Pineapple Crush. Both are very disease resistant, and vescana berries are almost as big as garden strawberries, so I’m thankful to have them, even if they do taste like canned strawberries.
And Honeyberries, Oh NO!
After three weeks of hanging on (the berries, not me), honeyberries, which are edible honeysuckles, are ready for a fair tasting. I wrote previously about the awful flavor of this new fruit and was instructed to let the berries hang till dead ripe.

The berries sampled this year were so ripe that each had to be plucked from the branch with my palm facing upwards beneath the berry; a mere touch would cause ripe ones to drop.
Rat-a-tat-tat-tat-tat (a drum roll). First to be tasted was the variety Solo. Reaction: spit it out quickly. Tart with bad flavor. Second fruit tasted was Sugar Mountain Blue. Also spit out, but not quite as quickly. And finally, Sugar Mountain Eisbär. Although retained in the mouth and having a hint of sweetness, this one, like the others, had bad flavor.
The flavor of honeyberries is allegedly like a mix of blueberry and raspberry. Not so! If you have space, plant blueberries or raspberries instead.

















 (The cooler is an insulated room cooled with an air conditioner that has been tricked, with a device called
(The cooler is an insulated room cooled with an air conditioner that has been tricked, with a device called 

 It’s cold-hardy to Zone 6. My plan is to grow it in a pot to bring indoors to a cool sunny window in late fall to spend the winter.
It’s cold-hardy to Zone 6. My plan is to grow it in a pot to bring indoors to a cool sunny window in late fall to spend the winter. mpost? Interested in details about how to make gourmet compost? This is a reminder that on Wednesday, September 23, 2020 from 7-8:30pm EST, I’ll be hosting a webinar about composting. For more information and registration, go to
mpost? Interested in details about how to make gourmet compost? This is a reminder that on Wednesday, September 23, 2020 from 7-8:30pm EST, I’ll be hosting a webinar about composting. For more information and registration, go to 




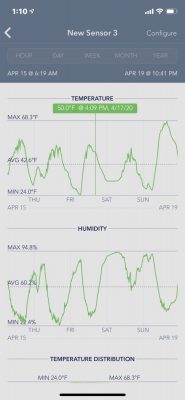
 Great. Even better, temperature (as well as humidity) is recorded, and can be displayed graphically or downloaded to my computer. So I didn’t have to be awake to find out the mercury hit 32.5°F at 12:16 AM on the night of April 17th and stayed there until it began rising around 7 AM.
Great. Even better, temperature (as well as humidity) is recorded, and can be displayed graphically or downloaded to my computer. So I didn’t have to be awake to find out the mercury hit 32.5°F at 12:16 AM on the night of April 17th and stayed there until it began rising around 7 AM.